Starfruit Barcode Technology
Yes, signatures are mandatory for all transfers according to ASCLD/LAB®. See below the extract of ‘Changes made in 2001 ASCLD/LAB® Accreditation Manual,’ but bar code is not for the purpose of recording transfers alone. Bar code is to make transfers easily by scanning without human’s typing.
To number a few purposes of barcode technology may include the following:
Ø Users do not have to type certain formatted standard characters,
Ø System identifies objects that are evidence in this case and users, and
Ø System trigs certain computer events based upon the identification.
 Consequently, using bar code can
eliminate clerical errors and elevate staff productivity.
Consequently, using bar code can
eliminate clerical errors and elevate staff productivity.
However, bar code alone does not authenticate and bind the unique characteristics of a user to the most important document of the crime community: chain of custody.
A valid paper-based chain of custody must have inked signatures of the recipient of evidence. A valid electronic paperless chain of custody must adhere to the specification of electronic signature. There are precedents of how court held validity of electronic signature to assist forensic laboratories in evaluating the court admissible electronic signature.
Be
aware that barcode technology is only as good as eliminating clerical
errors. Barcode technology has nothing
to do with paperlessness. Bar code
technology alone cannot make valid court admissible electronic chain of
custody. Bar code technology by
itself only achieves the purpose of data records.
Chain of custody
The
definition of chain of custody can be the transfer from examiner A to examiner
B, or from examiner A to vault, or from vault to examiner B. Particularly important, custody witness may
be required for criminal cases when transferring evidence. Signatures are required. Barcode is not a
signature. Without valid inked signature or electronic signature, chain of
custody of a forensic laboratory will be incomplete and illegal. Scanning barcode can easily document the
definition of chain of custody including sample identification, scientists’
identification, location identification, etc.
Be kindly advised that
advertisement such as ‘Chain-of-custody maintained via barcode’ is misleading. 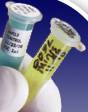
Starfruit Electronic Signature includes one license of Electronic Signature software that binds casework documents for each user.
Labeling
in Genetics
 The
difficulty is that the barcoding of vials to use in genetics, DNA sequencing,
virology, and related laboratory must be stored at extremely cold temperatures. Laboratory scientists report positive
identification of Eppendorf tubes and vials to liquid nitrogen temperature when
using Starfruit. Data Unlimited
International, Inc. provides and Starfruit prints labels specifically
engineered to withstand the extreme cold temperatures and adhere well to small,
tight diameter vials and containers. Starfruit labels are Alcohol and DMSO resistant; moisture
resistant in addition to being cold resistant. Starfruit organizes your label printing for laboratory functions
like tissue culture, freezer stocks, and embryo storage.
The
difficulty is that the barcoding of vials to use in genetics, DNA sequencing,
virology, and related laboratory must be stored at extremely cold temperatures. Laboratory scientists report positive
identification of Eppendorf tubes and vials to liquid nitrogen temperature when
using Starfruit. Data Unlimited
International, Inc. provides and Starfruit prints labels specifically
engineered to withstand the extreme cold temperatures and adhere well to small,
tight diameter vials and containers. Starfruit labels are Alcohol and DMSO resistant; moisture
resistant in addition to being cold resistant. Starfruit organizes your label printing for laboratory functions
like tissue culture, freezer stocks, and embryo storage.
Storing samples in freezers using small vials presents issues such as:
Ø ![]() Made
of plastic or glass, some vials have special silicone coatings to avoid spilled
liquid.
Made
of plastic or glass, some vials have special silicone coatings to avoid spilled
liquid.
Ø Tight diameter tubes or vials require labels to stick well around the curve.
Ø While you need to stick small labels to small tubes or vials, you still have to see through the side of the containers.
Ø Labels must resist repeated freezing and thawing cycles.

Starfruit prints to many label sizes for vials and tubes
to solve these challenging issues.
These labels are used particularly with Eppendorf tubes and microtiter
plates. Images shown are actual sizes. DUII makes labels any size to meet your need.
By choosing your label size and layout carefully, you may make it easier to
apply the labels and help organize your operations.
Barcode Standard and Definition
A Barcode
Symbology defines the technical detail of a particular type of barcode: the
width of the bars, character set, method of encoding, checksum specifications,
etc. Starfruit users are interested in the general capabilities of a particular
symbology (how much and what kind of data can it hold, what are its common
uses, etc) than in the technical detail.
The sections
below provide information about specific types of barcodes:
Numeric-only barcodes
· EAN-13: European Article Numbering international retail product code
· EAN-8: Compressed version of EAN code for use on small products
· UPC-A: Universal product code seen on almost all retail products in the USA and Canada
· UPC-E: Compressed version of UPC code for use on small products
· Code 11: Used primarily for labeling telecommunications equipment
· Interleaved 2 of 5: Compact numeric code, widely used in industry, air cargo, other applications
· Industrial 2 of 5: Older code not in common use
· Standard 2 of 5: Older code not in common use
· Codabar: Older code often used in library systems, sometimes in blood banks
· Plessey: Older code commonly used for retail shelf marking
· MSI: Variation of the Plessey code commonly used in USA
· PostNet: Used by U.S. Postal Service for automated mail sorting
Alphanumeric barcodes
· Code 39: General-purpose code in very wide use world-wide
· Code 93: Compact code similar to Code 39
· Code 128: Very capable code, excellent density, high reliability; in very wide use world-wide
· LOGMARS: Same as Code 39, this is the U.S. Government specification
2-Dimensional barcodes
· PDF417: Excellent for encoding large amounts of data
· DataMatrix: Can hold large amounts of data, especially suited for making very small codes
· Maxicode: Fixed length, used by United Parcel Service for automated package sorting
· QR Code: Used for material control and order confirmation
· Data Code
· Code 49
· 16K
Starfruit’s output uses code 128
barcode standard and DUII customizes to meet various formats.
For input, it depends on the barcode reader. Most bar code
readers support code 39, code 128, UPC-A, Codeabar, EAN/JAN-8, Plessey, 2 of 5,
and UCC-128.